“With technological advancements, the world has become more sophisticated and modern for sure but at the same time, it has become more dangerous and risky and this is what most people do not take into account.”
Before getting into the gist or core discussion of this topic, it is advisable to know what a ransom ware is and its purpose.
What is ransomware ?
A ransomware is a piece of malicious software that takes possession and infects a whole computer system or a network of interconnected devices leading to a system crash or access block usually of a threatening nature whereby an amount of money has to be paid in order to release the computer system from inactivity and gain access to the system. In simpler terms, a ransomware is a malicious software that blocks access to the victim’s data and threatens to publish or delete it until a ransom (an amount of money) is paid. This is why it has been named ransomware (malicious software that causes damage to a computer and asks for money in return so as to restore the computer system and the victim’s files).
That said, it is good to know that there are generally two types of ransomware that exist namely: simple or ordinary ransomware and cryptographic ransomware (crypto-viral extortion).
What is a simple or ordinary ransomware ?
An ordinary or simple ransomware is one which takes possession over a computer system and blocks access to the user (which is known as the victim). In the case of an infected computer system with a simple ransom- ware, a reverse technical operation can be carried out by an expert or IT knowledgeable person. However, it is to be noted that in this case, ransom is demanded by the perpetrator but it is equally true that the hacker or the individual behind the attack can be traced through certain procedures and operations (track down method) and if the culprit is found, legal actions can be taken accordingly.
What is a cryptographic ransomware (Crypto-viral extortion)
A cryptographic or crypto-viral extortion ransomware is one which is much more advanced in nature and is near to impossible to be resolved unless the ransom is paid. In the design of this malicious software, there is the use of a technique called crypto-viral extortion in which the ransomware encrypts all the data and files of the victim, thus making them inaccessible. The data and files of the victim user are blocked with a set of keys, known as the encryption key or code for which a ransom has to be paid within a period of time in order to get the decryption key or code which will be used to recover the computer system and the files of the victim user.
In a crypto-viral extortion ransomware attack, it is usually very difficult to reverse/restore the state of the computer system and the files even through complex computational techniques as the control is undertaken by the perpetrators through the malicious crypto-viral piece of software that has infected the computer system. In this sense, it becomes equally tedious to trace the digital currencies that are used by the perpetrators (such as Ukash and Bitcoin) for ransom purposes and therefore, the culprits are most of the time untraced due to the use of the cryptographic ransomware (crypto-viral extortion) which makes the tracing operation difficult and highly complex.
How does a computer system get possessed by malware ?
An instance which most people are not familiar with is how do they become victims of ransomware attacks or any other kind of cyber-attacks (malware attacks such as virus attacks, spyware attacks etc.). There are many ways through which a computer user invites cyber-attacks and the first one is through careless internet and web surfing. Very often, while surfing on the internet, computer users tend to click on ads that are published on a website and this is where the root of cyber-attacks remains.
Usually, not all ads that are published on websites are safe as most of the time, they basically conceal external links that will direct the user to unsafe or tempting websites or pages while some ads conceal malicious software (malware) such as viruses, spywares and/or ransomware that downloads automatically into the user’s computer when clicked. A different way as to how computer users become victims of cyber-attacks (malware attacks) is through visiting untrusted websites whereby they are often prompted to sign up as a member in order to benefit certain privileges.
Once they do as they are asked, that is, they provide their name, email, etc. they are sent an email of confirmation which is actually a virus or spyware or ransomware in disguise and once they click on the confirmation link or button, the camouflaged malware gets downloaded automatically in their computer. Yet, another instance which is a potential way to invite malware into one’s computer is through downloads.
Whether it is music (or any other form of media), a program (software), a game, or a picture; if it has been downloaded from an untrusted or a non-secured website, the content which has been downloaded is sure of containing malware and if executed without a proper security scan, the malicious effects of the downloaded content gets activated instantaneously.
Still in this sphere of how computer users become victims of malware attacks, another potential way to invite malware is through careless use of social media. Very often, there are links that are posted on social media websites like Facebook by people who are unknown to us. The links are posted in such a way that they tempt and attract social media users to click on them and soon after they are directed to unknown pages or websites whereby in the background, malicious content or malware get downloaded automatically without the prior knowledge of the user.
Finally, computer users become victims of malware attacks (viruses etc.) through the exchange/transfer of files and contents by using infected mediums (drives, discs or disk) such as virus infected pen-drives whereby one infected transfer medium infects a computer system as the malware travels along with the files/documents that are being sent to the receiver computer system.
Ultimately, computer users become victims of malware attacks due to careless reading and understanding of prompts that appear on the net or while installing an unknown software. While browsing on the internet, it may happen that users accept all that they are being asked (example; prompts that tell users that their computer is infected or an important plugin is required to be installed to enhance performance) and by doing so, the malicious effects of the installed content get activated when the users run them, that is, executes them.
The same applies for the installation of software (unknown or known programs) where without paying too much attention to the process of installing the new software, users end up by installing third party extensions or programs that are infected with malware and thus when the program is installed and run, the effects of the infected extension or program gets activated which then causes harm to both the computer system and the user. In addition, a computer user may be a victim of a malware attack through his/her participation in downloading pirated software, music or any other content in which there is the exchange and crack of copyrights, patents and licenses which is legally not permitted and in this practice, the computer user may be at high risk of being attacked by malware.
What happens is that, when downloading contents from such sites, computer users think that the downloaded content is safe (without even knowing that malware or other malicious software are attached to the content they are downloading) and once they start the installation process and the content gets installed, they start experiencing malfunctions and faults (which is actually the effect of the malware that gets activated).
Lastly, the absence of a good antivirus or anti-malware program on the computer system is quite risky and inviting enough for malware or malicious pieces of software to cause harm to one’s computer system.
How does a malware attack and infect a computer system ?
The initial answer to this question is that it all begins with a click! A simple careless click!
Bearing the name of trustworthy software or an important plug-in, the downloaded infected file when clicked by the user activates the effect of the malicious piece of software which then infects the computer where the core system (the Operating System) becomes unstable and starts to function weirdly. For instance, Trojans (a sub category of computer virus) is very deceitful as it shows itself as a useful program or plug-in initially by bearing the name of trustworthy software (such as media conversion programs or system cleanup programs) and therefore it tempts the user to install it and once it has been installed and executed, its malicious effects get activated whereby it starts destabilizing the computer system causing the functioning of the core system to be faulty and thus has a direct impact on the existing programs (legitimate software) of the computer.
However, the effects of the malware vary considerably as their built and complexities are not the same and in this way, the effect of a virus attack or a spyware attack or ransomware attack will be different. In terms of a virus attack, the computer will be still usable but with instabilities and malfunctions. For example, the files or information of the user stored on the computer may get deleted or corrupted after which they can’t be restored or recovered. Similarly, strange programs (infected software) might get installed automatically without the prior idea of the computer user and eventually those programs will jam the hard drive of the computer which decreases its performance.
More seriously, due to the ongoing instability caused by the virus attack, the computer system might shutdown by itself or get restarted automatically which represents a serious threat to the user as if the situation is not handled properly and appropriate actions are not taken, it might lead to an absolute system crash which will result in a big loss to the user as this situation is irreversible.
Generally, viruses are considered as pieces of malicious software that can be resolved and removed completely through proper procedures but their severity varies as some viruses might be mild (it does not cause too much damage to the computer except causing annoyances – minor instabilities) while some might be very fatal as they cause severe damage to the computer system by destabilizing the system completely (where the virus takes complete possession of the computer by creating a backdoor loophole in the system which gives access to the hackers or perpetrators to take control of the victim computer system).
In this sense, if the virus is not removed from the computer system in the early stages, it can lead to very difficult situations as they are known to get themselves replicated and reproduced (copy of their own source code) whereby they will eventually take over the computer system completely, infecting existing legitimate programs (causing the programs to run with anomalies and faults) and slowly infecting the core system (the bootstrap loader as well as the Operating System) which potentially leads to a system crash.
Similar to the infection/attack process of viruses, spywares are somewhat different in terms of execution and malicious effects.In terms of a spyware attack, the situation will be alike to that of a virus attack, that is, the computer will be still in a state of usability except for the fact the user will be not be aware of its presence. The reason behind this is simply because of the slyness of spywares (they usually affect the computer in a very discrete manner).
Once a spyware takes possession of a computer system, it executes its effects in the background without the prior idea or knowledge of the user and in its case; it will not cause any major abnormal functioning or instability, but will perform other tasks, that is, spying on the victim computer system and stealing information from the same computer system. In more details, what happens exactly is that the spyware spies on all the computer related activities of the user and keeps track of every single operation that is carried out. In parallel, the spyware transfers and copies all the data/files/information stored on the victim computer to the source drive (from where it has been downloaded – basically the computer of the spyware creator) whereby the perpetrator gets access to all the files the spyware has transferred (including personal and confidential information/documents/files) through which he/she can control the victimized computer system discretely by the backdoor loophole which the spyware has created.
In this way, when a spyware attacks a computer system, the perpetrators become aware of the status of the victim user and very often, if the victim is a potential gold giver, the perpetrators plan a ransomware attack where they block the computer system with an encryption key or code. However, there exist harmless types of spywares also that are designed for professional use only (example in office setups) whereby all activities that are carried out by employees on their respective computers are monitored/spied to make sure that office and professional work are being carried out dutifully. Coming to the instance of ransomware attacks, the case is completely different from those of spyware and viruses as ransomware is far much more fatal and chaotic than the two previously explained ones. In a ransomware attack, the victim computer or computer network is blocked and is basically unusable as the malware is built in such a way that it overtakes the computer system completely.
That said, a ransomware, in most cases, is preceded by a spyware attack operation where much information and data (personal, professional and confidential) are gathered by the perpetrators which paves the way for a potential ransomware attack where the victim computer system is blocked and taken under the control and possession of the perpetrators whereby they are the only people to unlock the system (after the demanded ransom/amount of money is paid) through a decryption key which they possess. Within a ransom ware attack, the perpetrators hold possession of all the contents on the victim computer system due to which their threats get bolder and more fearful as if the ransom is not paid, they can do anything with the contents which can prove to be chaotic/fatal/costly to the victim. However, the big question that remains is that: How does the ransomware attack take complete possession of a computer system and cause it to be blocked with a series of encryption keys?
The answer to this question is quite simple! A ransomware usually disguises itself as a Trojan (a sub category of virus) that attaches itself to content on the net (downloadable materials such as pirated software, plug-ins or media content usually found on websites). When downloaded and installed, the hidden Trojan starts executing its malicious effects eventually until it reaches a standpoint after which the ransomware will surface up. Now, how does the disguised ransomware surface up from the Trojan in which it was camouflaged? The answer to this part question is equally simple: At the standpoint stage, the computer might restart/shutdown by itself or the malware might show up a tricked message on the screen (which the user accepts without knowing that this is a malicious operation in disguise) which says something like that “The computer needs to be restarted in order for the updates get installed...”. In both cases, when the computer will restart or shutdown, the ransom ware (which was camouflaged in the Trojan) will get activated instantaneously and therefore, it takes control of the core system (by infecting and destabilizing it) which shows its results in the next reboot, that is, when the computer will be switched on again, whereby the user will be no longer able to enter the system because of an encrypted system lock which requires a ransom payment in order to get unlocked with a decryption key.
What are the risks involved if a victim does not pay the ransom demanded ?
There are a considerable number of risks/consequences that get associated with a ransomware attack if the victim refuses to pay the ransom (the amount of money demanded against the unlocking of the system) and they will all prove to be chaotic and fatal to the victim. It is good to remind people that in such situations, like that of a ransomware attack (usually that of a cryptographic/crypto-viral extortion and about which we have been referring to up till now), even the best of IT Security personnel fall helpless because of the cryptographic technique used by the hackers/perpetrators in the ransomware attack where there is the use of an encryption key to lock the system (which the hackers have) and a decryption key which is needed (which the hackers also have) and will be provided only after the ransom has been duly paid through either Bitcoin or Ukash (digital crypto-currency systems used to transfer money electronically with encryption technique between individuals) which if not accepted or paid, may prove very costly to the victim (and therefore this situation makes it very difficult for IT professionals to resolve the problem as the correct decryption key is required for the system unlock without which the computer system might become unusable).
In that sense, the victim must be aware that in a ransomware attack, the perpetrators hold complete control of their computer system as well as their files/documents/information (which can be personal, private, professional and/or confidential) and therefore, they can do anything with them (like publishing the private pictures of the victim on the net with the sole aim of causing defamation to him/her or deleting important documents/files/information of the victim resulting in an instance of data/information loss or even hacking the various accounts such as Gmail or Facebook or any other account of the victim which can result in serious problems) among others. Similarly, another instance that can arise if the victim refuses to pay the ransom is that of hardware loss. As the term signifies it all, it is the actual loss of hardware, that is, the loss of the computer system. How is this so? If the victim does not pay the ransom within the deadline span given, the perpetrators will take advantage of the situation to infect and cause more harm to the computer system by injecting more malware and viruses which will cause the system to become completely unstable leading to an absolute system crash (an irreversible situation) and all this will happen without the slight idea of the victim user as he/she will be still seeing the blocked screen but alas, in the background, the perpetrators have already done their malicious deed. Overall, these are the consequences.
Nevertheless, there are some slight variations in ransomware attacks where the attack strategy differs based on the ransomware author (the hacker or perpetrator). As example, the WannaCry ransomware attack was huge and massive for sure but was slightly different from others in connection to the risks and consequences linked to non-payments of ransom. WannaCry, on its side, gave a deadline of three days to pay the amount which shall get doubled after the three days period and after seven days, their data, files, information and everything that were maliciously encrypted will get deleted and lost forever. However, the most bitter consequence of the non-payment of the ransom will cause the inaccessibility to the computer system for six months and deletion of all encrypted content on the system (this step of WannaCry aimed poor computer users who will be unable to pay the ransom in Bitcoin) and therefore adds to the risks and consequences of not paying money (ransom).
Wannacry, Golden eye and Petya/Notpetya ransomwares
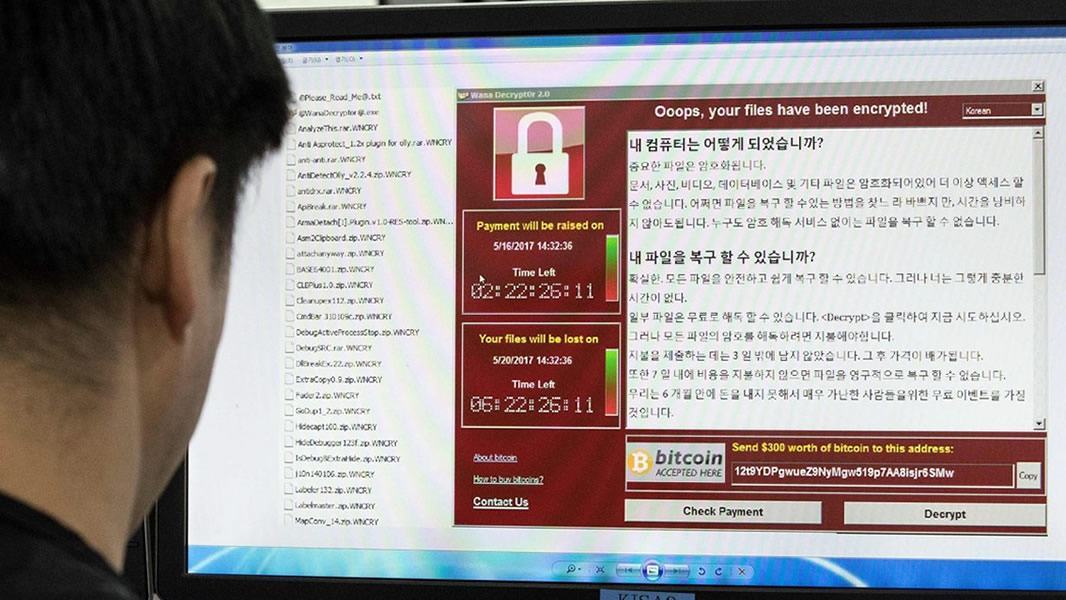
Like explained earlier, a ransomware is a malicious piece of software that camouflages itself through a virus and causes harm to a computer system by asking a ransom in return to restore everything back in order. In this section, we are going to have a look at some of the latest ransomware that have attacked companies as well as agencies around the world causing major problems. Similarly, we are going to have a look at these malwares and their impacts/effects in a much detailed manner. A big question to which the answer is still unknown and many among us are still in the dark, thankfully, through this article, the audience will acquire a much better and clearer view about those recent cyber-attacks via ransomware. The latest one named ‘WannaCry’ ransomware, also known as WannaCry Ransomware Attack was a massive cyber-attack recorded in May 2017 at a global level (worldwide attack) whereby its initial outbreak was through a crypto-worm (a subcategory of the computer virus enlistment) which basically targeted computers running the Windows Operating System also known as Windows OS by encrypting the data and files of the victims with demands of ransom payments in the Bitcoin crypto-currency. It is to be noted that the most vulnerable systems that were infected by the crypto worm WannaCry ransomware were computer systems running the Windows 7 OS (statistics reporting a 98% of Windows 7 systems being affected by the malware).
How did WannaCry propagate itself around the world ?
The WannaCry malware series replicated itself through the use of EternalBlue, known to be an exploit of the Windows’ Sever Message Block (SMB) protocol. Used in computer networking, a SMB operates as an appli-cation layer network protocol, used for providing shared access to files, devices and serial ports as well as the various miscellaneous communications that happen between nodes on a network whereby there is also a kind of inter- process communication. It is to be noted that SMB involves mostly computers that run Microsoft Windows systems (OS) and this is how the WannaCry ransomware got spread over the world affecting over 250,000 computers that were Windows based.
How did those 250,000 computers get infected with the WannaCry ransomware?
There have been many speculations about the infection spread by WannaCry ransomware that computers were infected through spam/malicious emails that were sent to the targeted users (worldwide users of Windows) by the perpetrators but however, they were all proved wrong after due technical and computational research that were carried out by IT Security Intelligence professionals. How did it infect those 250,000 computers then?
Indeed, the WannaCry ransomworm or ransomware was not distributed through spam/infected emails but in fact, it was rather spread around the world via an operation that hunts down vulnerable public facing SMB ports and then it used the alleged leaked EternalBlue exploit to get on the network and equally used another exploit known as the DoublePulsar to establish persistence and allow for the auto-installation of the Wanna-Cry ransomware on the network and exploit system.Just to enlighten the audience about the DoublePulsar exploit, the DoublePulsar is a backdoor malware that is closely tied to EternalBlue exploit where EternalBlue provides checks to determine the existence of DoublePulsar.
This particular malware uses an APC (defined as Asynchronous Procedure Call) to inject a DLL extension file into the user mode process mode. Once injected, exploit shell code is installed to maintain persistence on the target system after which the backdoor code are removed from the system after successful verified installation. As a last analytical response in regard to those 250,000 infected/attacked computers, it is affirmed that they were all vulnerable machines which were easy preys of the WannaCry ransomware which made its attack through the SMB TCP port 445 and RDP TCP port 3389 and thus it spread its infection through the network causing thousands of computer systems running the Windows Operating System to get infected and attacked due to this loophole of some ports.
Nevertheless, the ability of the coding of the malware (WannaCry Ransomware) to beacon out to other potential SMB targets allows it to propagate to other vulnerable machines on connected networks and this is what made it become so dangerous and fatal. The ability to spread and self-propagate caused widespread infection without even any user interaction with the machine.The WannaCry ransomware attack was huge and massive for sure but was slightly different from others in connection to the non-payments of ransom. WannaCry, on its side, gave a deadline of three days to pay the amount of $300 which shall get doubled after the three days period ($600) and after seven days, the data, files, information of the victimized user and everything that were maliciously encrypted will get deleted and lost forever. However, the most bitter consequence of the non-payment of the ransom will cause the inaccessibility to the computer system for six months (blocked access) and deletion of all encrypted content on the system whereby this step of WannaCry aimed poor computer users who will be unable to pay the ransom in Bitcoin and therefore this adds to its severity level as a malware.
On the same line, GoldenEye ransomware is another member of the malware family like WannaCry and has been known to cause major problems with the support of the Petya ransomware which continuously gained its maturity since 2016, transforming into one of the most dangerous threats to the cyber world after WannaCry which was reported and recorded in this year itself, that is, June 2017. It has been found, through research and computational analyses that infections by GoldenEye ransomware and Petya/NotPetya ransomware were due to a compromised update of the MeDOC accounting software which is widely used in Ukraine and European countries (Accounting and Financial firms of Europe) and the use of phishing emails (used by GoldenEye).
Petya/NotPetya which spread its infections through a compromised update file of the MeDOC accounting software initially targeted Ukraine and parts of Europe that caused thousands of cyber victims globally while GoldenEye mainly targeted Germany and neighboring countries in Europe. In this regard, the Petya/NotPetya ransomware became one of the most recent highly dangerous malware due to its noticeably higher severity than WannaCry and its complex maturation which began since 2016 along with the GoldenEye attack.
The Petya/NotPetya ransomware is known for having caused major instabilities in affected systems across its targeted victim range namely the Ukraine transportation department, banks, firms and agencies due to its high malicious effects as compared to WannaCry. However, the WannaCry ransomware has been known to be a bit more powerful than Petya ransomware (though both are worms) as it attacked a larger mass of computer users and firms worldwide.
Nevertheless, the Petya/NotPetya and GoldenEye ransomware are far more fatal as they laterally compromise the whole system blocking all possible access until the ransom is paid. WannaCry, on its side, allowed for a free decryption of some encrypted files (around 1 to 3 files only) before paying the ransom whereas GoldenEye/NotPetya and Petya/NotPetya ransomware did not even allow that much, blocking initial access to the system itself.
The recent Petya/NotPetya ransomware attack made its malicious effect through simulated updates of the MeDOC Accounting software (which were actually a cover-up of the malicious tasks and operations that were running in the background) and an initial disguised disk check operation (which was also a cover-up process) at the startup of the system (booting session where the operating system loads) after which the ransom note was displayed as a command line interface model blocking all possible access.
At this stage, the user could not enter the system as everything got corrupted and encrypted and therefore made the system blocked and inaccessible until the ransom was paid in Bitcoin as demanded making the ransomware a more complex, dangerous and fatal than WannaCry.
Similar to the Petya/NotPetya ransomware, GoldenEye simulated a range of phishing emails that looked legitimate due to the tailored development by the hackers (which contained attachments and links that concealed the ransomware in complete disguise) and after openingor clicking on the links would download the worm automatically and cause its installation discretelywhere its malicious operationsgot initiated in the background without the basic idea of the users. It was in the next system reboot that the malware (GoldenEye) effected its final task through the interruption of the booting session which got infected and corrupted previously through the malicious and infectious operation in disguise of attachment opening/downloading or link check causing the core to get unstable and corrupt with errors. It was then at that stage (the booting session stage) where the ransomware published the ransom note in a command line interface model to the users blocking all possible access to the system until the demanded ransom was paid completely (resembles the Petya/NotPetya ransomware attack model) and it is in this context where these two ransomware are known to be more dangerous than WannaCry ransomware. Both GoldenEye and Petya/NotPetya ransomware are known to have affected hundreds of thousands of victims worldwide.
WannaCry Ransomware Attack (Recorded in May 2017): >250,000 computer victims worldwide
GoldenEye Ransomware Attack (Recorded in March 2016): Around150,000 computer victims worldwide This cyber-attack was made through phishing emails while Petya/NotPetya was still maturating
Petya/NotPetya Ransomware Attack (Recorded in June 2017): Around 200,000 computer victims worldwide
GoldenEye Ransomware Attack (Recorded in June 2017): Around 200,000 computer victims worldwide
Known as Petya/NotPetya attack to people, this GoldenEye ransomware version actually formed part of the fully matured Petya/NotPetya ransomware attack recorded in June 2017 which got spread through the compromised update of the MeDOC software affecting Ukraine and European countries.
The big question : Are computer users in Mauritius protected ? Are we safe ?
It is an undeniable fact that computer users are never safe and protected which indirectly answers the question that computer users in Mauritius are in the same basket equally as there is the use of internet to carry out tasks every day and therefore exposes the users to risks of being victims of malware attacks. However, that does not imply that computer users are totally vulnerable but in order to stay on the safe side, all computer users must take certain necessary precautions and must follow certain measures to reduce risks of being cyber-attack victims as though the internet is known for being a web of information, useful resources and other contents, it is also known to be the place where malicious individuals (such as hackers) plan and execute illegal moves in order to make black money through cyber-attacks (malware attacks, virus attacks, spyware attacks) and so on.
Moreover, in regard to the latest and recent ransomware (malware) attacks, people in Mauritius are informed to be more vigilant and careful while surfing on the internet as the danger has not yet been eliminated (here reference is being made to both WannaCry ransomware and Petya/NotPetya ransomware attacks). A kill switch for the malware which was developed by an IT Security researcher proved efficient as it slowed down the infection spread of the malware (WannaCry ransomware) but unfortunately it was identified by the hacker or group of hackers and an advanced technique to overcome/eliminate the kill switch was devised by them, which caused the malware spread to continue and infect more computers. As for the Petya/NotPetya attack, no kill switch was devised implying its free roam and existence on the internet and therefore users should be very careful while surfing on the internet, visiting websites and most importantly, while downloading, users should be very cautious. It is therefore with these words that it can be concluded that computers users in Mauritius are not completely protected and should be more vigilant while using the internet.
Who are those at risk of being cyber-attack victims ?
From a general perspective, it can be asserted that all computer users are vulnerable to cyber-attacks but there are certainage groups of users who are more vulnerable than others due to their incomplete awareness about the world of technology and computing; these groups are namely the early teenage group (including children of age range: 7-12 years) and elderly group (45-70+ years). Taking these age figures into account, users of the age groups mentioned above should be assisted at all times while using the computer and should be educated accordingly with the aim of making them aware about the possible dangers of the internet and computer based technology. Moreover, the reason behind the target of these age groups as being more vulnerable to cyber-attacks is formulated based on their careless use of the internet and computers. It is indeed a fact that these age groups use computers and the internet carelessly which arises the risk of being victims of computer criminals and therefore adds them in the category of vulnerable users. Effectively, these age groups use technology (i.e. the internet and computers) in a very unprotected manner (for example, the practice of careless clicks, that is, clicking on contents that are displayed on the net without knowing what they are actually, downloading any-thing from any website and so on) and these practices further enlist these groups as vulnerable users or users who are at risk of being victims of cyber-attacks. However, the lack of awareness or incomplete education in the field of technology equally forms part of the reasons behind the enlistment whereby the teenage group that includes children of age range 7-12 years hold an incomplete education about technology while the elderly group (45-70+ years) lack awareness about technology which make them easy preys of computer criminals and vulnerable users of technology.
The big question : should victims pay the ransom amount ?
The decision to pay or not to pay the ransom usually depends on the victim and in many cases which have been observed so far, the victims tend to pay the demanded ransom amount without knowing what awaits them later on. Based on my opinion, I would highly recommend and advise victims (if there are any such victims of cyber-attacks in Mauritius) NOT to pay the ransom and this recommendation is based on several reasons. Firstly, in nearly all cases (96 percent of cases); the user never gets back his/her files which were encrypted during the attack after payment of the ransom. Either the files have been modified and corrupted or have been deleted by the perpetrator. In the same way, it has equally happened that though the victim has paid the ransom amount, not all of his/her files are restored as many among the encrypted content get erased. On the other hand, based on the conditions stated in the ransom note, there have been cases where the perpetrators published private/confidential content of the user on the net causing the victim to become more vulnerable. In this sense, it is highly advisable not to pay the demanded ransom amount as there is no guarantee that what-ever which have been stated or promised in the ransom notice will happen after the payment.
What precautions should be taken to stay safe ? Tips and advice…
First of all, users should use their computer according to their level of expertise (that is, beginner, amateur etc) in order to ensure that they know what they are doing. Following that first step itself will make sure that users are using technology (in this case, computers) safely and appropriately. The use of internet is another stage of computer technology which comes afterwards and must be embarked upon only after proper and satisfactory mastery of the computer itself (that is, using the computer correctly, understanding its possible limitations etc) and knowing all the utilities and software, their uses and so on – That is, knowing the basics. In the same way, users should enforce security protocols such as passwords on their computer to prevent unauthorized access and thus keep their device protected and secured. Still on the ground of computer systems, users should also make sure that all their software are updated (up to date) in order to ensure that they are not outdated which implies their vulnerability to problems. In this sense, users must be aware that keeping their computer system and its components up to date (updated) is very important because it ensures the proper functionality of the computer (effective performance) and helps to be on the safe side as updates includes installation of latest and revised security patches for software and utilities ensuring secured use of technology. Moreover, users must make sure that their computer system is equipped with a good antivirus/antispyware software which will help to keep them protected from viruses, malware and other dangers at all times. In that direction, users should be equally aware that they should perform a security scan of their computer system at least twice a week though a daily scan is more recommended (but it all depends upon the frequency of using the computer) – users who use their computer everyday must perform a security scan through their antivirus/antispyware software at least three times per week to ensure that their computer system is safe, clean and protected from danger while the users who use their computer on a regular basis (not daily) are advised to scan their computer at least once per week to ensure that their system is clean, safe and protected from danger(virus, spyware, malware etc).
Similarly, users must ensure that their antivirus/antispyware software is up to date to affirm that they will be able to detect and diagnose latest threats and dangers and therefore be able to eliminate those threats promptly at the right time. Another security tool that must be ensured is running by users is the firewall. A firewall is one which prevents unauthorized access to one’s computer when using the internet or when connected online, and therefore helps to keep the user secured while the latter is online/surfing on the net – The activeness of the firewall must be checked by users and must be turned on at all times along with the antivirus/antispyware to ensure safety and constant protection of the computer and user against danger/malware/virus. Another step to be taken by users is to read well agreements/license agreements/installation procedures or processes when installing a program/software on their computer system – what happens in most cases is that users accept everything without even paying attention to what has been asked and thus land in problematic situations that are quite tedious to be resolved due to their incompetence to solve the problem. Therefore, users are advised to read well agreements and pay attention to installation procedures/processes while installing a program to make sure that they are installing the right product and that no third-party software or adware/foistware are being installed as they will prove to be detrimental to the computer system and user afterwards. Prior to the installation of the program, a nice tip to users is to perform a security scan of the downloaded file that will be installed later, that is, the executable file which looks like examplesoftware.exeneeds to be scanned to ensure that it is safe to be installed.
Coming to the use of internet, more precautions are needed to be taken as users are more exposed to potential risks. Basically, on the internet, the precautionary steps are divided into two main parts namely: Protection of Identity and Protection of Connection abbreviated as PoI and PoC. In terms of Protection of Identity (PoI), all users are advised to choose strong passwords for their accounts that they use online (example; Facebook and Gmail accounts, Yahoo Mail, Hotmail, Twitter, LinkedIn etc) in order to enforce their privacy and protection which is of paramount importance. Users must be informed that passwords are like the keys to their accounts and therefore they are responsible to set a unique, hard to guess and strong password to make sure that their accounts are not accessed by unauthorized people. As advice, passwords with varying specifications are the best; that is, passwords that contain numbers, lowercase and uppercase letters/alphabets, special characters are known to be complex and powerful thus proving to be secure and hard to crack. Moreover, users are advised to set a different/unique password for each account in order to keep them safe and secure. On the contrary, it is equally possible to set the same password for all the accounts but with varying tags (for example, users can use the password “exAmple123456” for all accounts by attaching different tags like gmailexAmple123456 for their Gmail account or hotmailexAmple123456 for their Hotmail account – the password will be the same one but will become unique and stronger by attaching varying tags. Still related to PoI, users are equally advised to be careful with emails, most specifically phishing emails and scams. Phishing emails are those emails that appear to be from legitimate sources such as a software company or bank or any company with which the user has done transactions previously. These emails will provide links to fake websites and most users get trapped leading to difficult situations such as account hacking, information theft and even identity theft. As a measure to stay safe and secure from these phishing scams, users are advised to verify the sender’s information well before clicking on any links or attachments, that is, they must check the sender’s email address, name etc and if in that verification process, they find something fishy, they have the urgency to discard/delete that email in order to stay safe from problems and cyber-attacks.
Also, users are highly advised to discard any pop-ups, emails, websites and links that appear while surfing the internet as they are all scams – some examples of such scams are pop-ups, emails, websites and links which display lottery wins, huge sum of money wins etc. In order to stay safe from these, users need to discard them and halt from clicking links associated to these scams as they are insecure and may contain malicious content such as malware, virus, spyware or even Trojans that can potentially infect their computer system. Another precautionary measure to stay safe on the internet is to limit the information you provide on social media and websites/chat-rooms. Users are advised NOT to give any sensitive information such as their passwords, PIN number or personal information as these information can become the weapon of malicious individuals where they can cause harm to the victim user in several ways. In terms of Protection of Connection (PoC), the most important initiating step that must be taken by all users is to verify the security enforcement of their wireless router (the device that enables a user to connect to the internet and provide Wi-Fi). The routers are usually set to WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)security levels by default; but unfortunately WEP security protocols are not that strong as compared to the two other protocols known as WPA/WPA2.
That is why, in order to enjoy secured connections, users are advised to set their router security to either WPA or WPA2 (defined as Wi-Fi Protected Access) which further enhances their router’s security. Nevertheless, users are advised to be very careful while using public networks (known as Wi-Fi hotspots) as these are insecure networks which are quite vulnerable. They are generally less secured and do not possess strong security protocols such as the WPA or WPA2 and therefore users are advised NOT to share sensitive information over these networks as instances of information theft or even identity theft may happen. However, that does not imply that public networks should not be used; in fact people should benefit these facilities and must use them but certain measures of precaution should be followed equally just to be on the safe side. Thus, while using public networks (Wi-Fi hotspots), all users are advised to turn off file sharing and network discovery. When turned on and using public networks, these features/options put the files of the user and their computer system at risk for being opened by anyone on the wireless network (by anyone, it is understood that hackers may be involved too) and therefore they should be careful while using these networks. As a tip to users, these network features/options can be found in Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center (for Windows OS users) while for Mac OS X users, these features/options can be found under System Preferences > Sharing. That said, another vital and most important step that should be taken for the Protection of Connection (PoC) under internet use by users is to check website security before performing any further action in their regard. In other words, users are advised to visit and surf on websites which possess a secure connection protocol. To check this, it is very simple, usually secured websites possess an SSL digital certificate which is installed on their server that ensures secure communication, interchange of data and most importantly, secure connection between the user, web browser and the website (web server) though encryption technology and to check this, their Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP) will appear as HTTPS which means Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure (example: https://www.google.com) is a secured webpage/search engine.
However, users must be still careful while visiting websites as not every website that runs an https:// protocol is obligatorily secured and must therefore be mindful of what websites they are visiting. Finally, users should be very careful with their downloads and should perform them from secured and trustworthy websites. As a last word in terms of advice and some tips, users should be careful and must use technology with precautions.
Professional tips at a glance (Summarised)
Users are advised to abide by the tips provided below to make sure that they are protected and safe:
- Always keep your computer system updated. Users can opt for automatic updates- They just have to turn that option [ON] on their computer system by going to Settings (machine/OS dependent)
- Always update your programs (software) to keep them running correctly and secure as updates include the installation of security patches which are important.
- If you don’t have an antivirus/antispyware program, make sure you get one. However, computers running Microsoft Windows OS have an in-built security program called Windows Defender. Make sure you turn it on and its firewall service as well to keep you protected. Always keep your security software updated for it to operate and function correctly.
- While connected to the internet, make sure your connections are secure and that your router/wireless router is set to WPA or WPA2 security protocols [This step requires the assistance of a network knowledgeable person or IT technician].
- While browsing the internet, act and behave smartly and avoid getting trapped by scams that roam freely on the internet and webpages. Avoid clicking on everything that you see and learn safe browsing. Users should also avoid clicking on ads though they appear legitimate as most of the time, those ads actually conceal malware, virus or Trojans which can infect your computer. So avoid clicking ads and browse safely!
- Visit websites that you know or heard about and make sure that they are trustworthy, secure and safe to surf and use. If you find the website fishy or weird, leave it immediately [exit from the website ASAP].
- Always verify the security of connection of a particular website. Make sure that the URL (the link that is seen on top of your browser) contains [https://] instead of [http://]. The links (URLs) of websites that have the [https://] protocol are secured and thus are safe to visit. However, though a website’s URL contain the [https://] protocol, be careful before entering the website and make sure you know the website that you are visiting as there are fake/malicious websites that pretend to be secured in order to attract users who become victims of adware/malware/virus. So always be careful!
- Avoid downloading content from any website you find on the internet. Always make sure that the website from which you are downloading is safe and secure. Once you have downloaded what you wanted, always perform a security scan of the material/content downloaded before using, executing or running it.
- Check your emails well before opening any attachments or clicking on any links associated to them. There are malicious emails (known as phishing emails) that may enter your mail inbox, so be careful. They often appear to be legitimate but there are always loopholes in them which distinguish them from valid emails, so always be careful and check for these loopholes before doing anything. If they are weird, delete them!
A list of recommended antivirus/antispyware programs (Software)
All computer users are advised to have at leastone of the following security software (programs) to ensure their protection and safety while using computers and the internet.
NOTE: Windows Defender is a good basic security program (antivirus) which is in-built in all computers running the Windows OS but it lacks advanced features which other effective antivirus/antispyware programs have and therefore, it is recommended to have an additional antivirus/antispyware program to stay protected and safe completely from threats and dangers.
The recommended security (antivirus/antispyware/anti-malware) programs (software) are as follows:
- MalwareBytes Anti-Malware
- McAfee Total Protection / McAfee Antivirus Plus 2017
- Kaspersky Total Security / Kaspersky Antivirus 2017
- Bitdefender Antivirus Plus 2017
- Symantec Norton Antivirus 2017 / Norton Internet Security 2017
- Avast! Pro Antivirus 2017
- ESET NOD32 Antivirus 10
A MESSAGE TO THE CONCERNED AUTHORITIES : ICTA, NCB AND MINISTRY OF TECHNOLOGY, COMMUNICATION AND INNOVATION
In order to stay safe and protected, computer users need appropriate resources and materials which are not accessible sometimes due to financial limitations. Thereby, request is being made to the concerned authorities and the ministry (Ministry of Technology, Communication and Innovation) as well to devise schemes or grant frameworks to provide computer users with facilities and benefits as far as their security of computer use and internet involvement is concerned. Facilities might include the grant scheme of security programs (antivirus or antispyware software) which are made available online (on the government online portal, for example) where users will be able to access and download them freely without any costs (as it is the case so far where users have to buy those software in order to benefit all security features and usually discourages them to proceed due to their financial limitations). In this way, we can hope for a more secure Mauritius with all the computer users of our country protected and safeguarded.
Is there any solution to put an end to malware and cyberattacks ?
However, as of now, no concrete solution has been built or developed yet but the good news is that research methodologies to eradicate such instances are being carried out by IT security experts and IT companies (at international level) and in my point of view, I strongly believe that sooner or later, this problem of malware cyber-attacks will come to a halt leading to an end eventually but there is no guarantee of that. A kill switch (a piece of coding to combat malicious/infected software) for the WannaCry ransomware was developed by an IT security researcher but unfortunately, it was counter attacked by the perpetrators/hackers. In the meantime, it is advisable that computer users take necessary precautions while surfing on the net as it is the most vulnerable space of computer technology where malware are circulated in various undercover forms that look for computer victims. If users abide to the list of tips and advises provided in this article, they are going to stay safeguarded and protected always, no matter the threat that is roaming on the internet.
 J'aime
J'aime














